In today’s dynamic B2B landscape, businesses are increasingly recognizing the strategic importance of reverse logistics. Traditionally, logistics focused on the forward movement of goods—from manufacturers to end-users. However, reverse logistics, which involves the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distributor for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal, is gaining prominence. This shift is driven by factors such as sustainability concerns, cost optimization, and the need for enhanced customer satisfaction.
Understanding Reverse Logistics in B2B Context
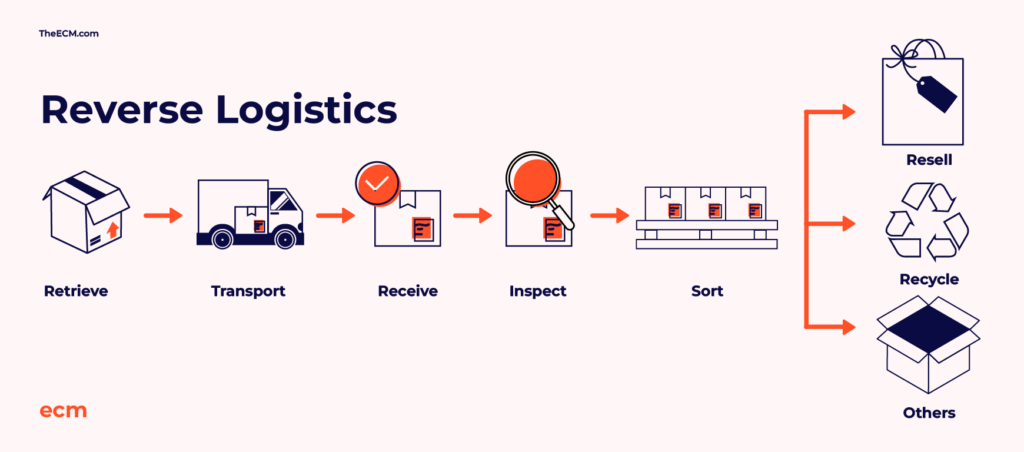
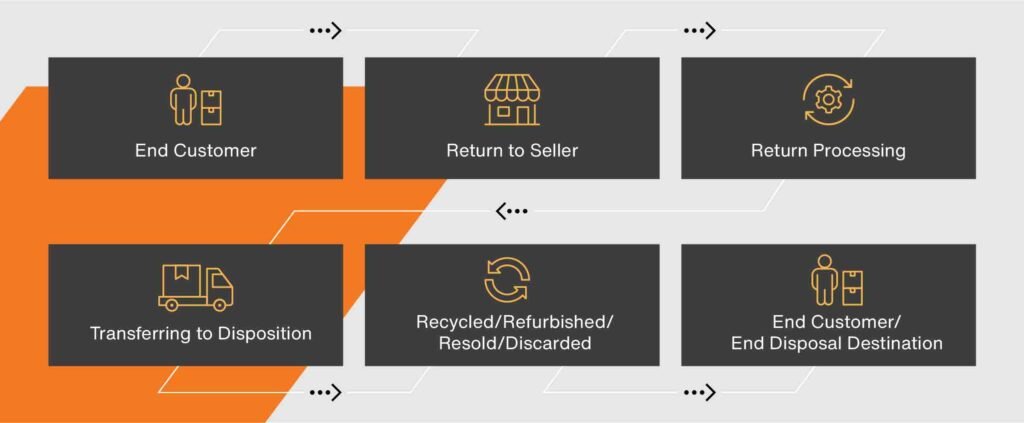
Reverse logistics encompasses all operations related to the reuse of products and materials. In a B2B context, this includes the return of goods from businesses to suppliers or manufacturers for various reasons, such as defects, excess inventory, or end-of-life products. The process involves several stages:
- Return Initiation: The process begins when a business identifies the need to return goods. This could be due to defects, overstock, or other reasons.
- Transportation: The goods are transported back to the supplier or manufacturer. Efficient transportation is crucial to minimize costs and environmental impact.Vogue Business+6DHL+6varuna+6
- Inspection and Sorting: Upon arrival, products are inspected to determine their condition and decide on the appropriate action—whether to refurbish, recycle, resell, or dispose of.uroute.co+1DHL+1
- Processing: Based on the inspection, products are processed accordingly. This could involve repairs, refurbishment, or recycling.
- Disposition: Finally, products are either returned to inventory, resold, recycled, or disposed of, depending on their condition and value.DHL+1Vogue Business+1
The Strategic Importance of Reverse Logistics
1. Enhancing Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
In the B2B sector, customer satisfaction is paramount. An efficient reverse logistics process ensures that businesses can handle returns, exchanges, or repairs swiftly and effectively. This responsiveness not only resolves issues promptly but also builds trust and strengthens business relationships. A study by DHL indicates that 68% of B2B buyers scrutinize their suppliers’ return policies before making a purchase, highlighting the importance of a robust reverse logistics strategy in influencing purchasing decisions. DHL+3Warehousing Express Logistics+3varuna+3DHL
2. Cost Optimization
While reverse logistics involves additional processes, it can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By efficiently managing returns, businesses can recover value from returned products through resale, refurbishment, or recycling. This approach reduces the need for manufacturing new items, lowers disposal costs, and minimizes inventory waste, leading to greater overall cost savings. UCS Logistics+4DHL+4Warehousing Express Logistics+4
3. Promoting Sustainability
Reverse logistics plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability within the supply chain. By facilitating the return, reuse, and recycling of products, businesses can minimize waste and reduce their environmental footprint. This aligns with the growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility and can enhance a company’s reputation among environmentally conscious stakeholders. Conner Industries
4. Regulatory Compliance
Many industries are subject to stringent regulations regarding product returns, recycling, and disposal. An effective reverse logistics system ensures that businesses comply with these regulations, thereby avoiding potential legal issues and penalties. This is particularly important in sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, where regulatory requirements are often complex and stringent.
5. Data-Driven Insights
Reverse logistics provides valuable data that can be analyzed to gain insights into product performance, customer preferences, and operational efficiency. By analyzing return patterns, businesses can identify common issues, improve product quality, and refine their offerings to better meet customer needs. This data-driven approach supports continuous improvement and strategic decision-making.
Implementing an Effective Reverse Logistics Strategy
1. Leverage Technology
Integrating advanced technologies such as RFID, barcode scanning, and GPS tracking can enhance the efficiency and transparency of the reverse logistics process. These technologies enable real-time tracking of returned goods, accurate inventory management, and streamlined processing, thereby reducing errors and delays. Shiprocket Cargo+4varuna+4DHL+4uroute.co+2Onepak+2DHL+2
2. Standardize Processes
Developing standardized procedures for handling returns, inspections, and processing can improve consistency and efficiency. Clear guidelines and workflows ensure that all returns are managed systematically, reducing confusion and potential bottlenecks.Onepak
3. Collaborate with Partners
Partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) can offer expertise and resources that enhance reverse logistics operations. 3PLs can manage transportation, warehousing, and processing of returns, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies while ensuring efficient handling of reverse logistics. UCS Logistics
4. Monitor and Optimize Performance
Regularly monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as return rates, processing times, and cost per return can help identify areas for improvement. Continuous optimization of the reverse logistics process leads to enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Overcoming Common Challenges
1. Managing Return Fraud
Return fraud can be a significant issue in reverse logistics. Implementing stringent verification procedures, such as requiring proof of purchase and inspecting returned items thoroughly, can help mitigate this risk.Warehousing Express Logistics
2. Handling Complex Returns
Some products, such as specialized equipment or hazardous materials, require specialized handling during returns. Developing specific protocols for these types of returns ensures safety and compliance with regulations.
3. Addressing Capacity Constraints
An influx of returns can strain existing resources. Planning for peak return periods and scaling operations accordingly can prevent bottlenecks and ensure timely processing of returns.
Case Studies: Successful Reverse Logistics Implementation
1. Electronics Manufacturer
An electronics manufacturer implemented a reverse logistics system that included automated return processing and refurbishment capabilities. By using data analytics and automated inspection technologies, the company identified common faults in returned products and improved their quality control processes upstream. As a result, they reduced return rates by 22% over a 12-month period. Additionally, refurbished items were resold in secondary markets, generating a new revenue stream and cutting e-waste significantly.
2. Automotive Industry
A leading automotive parts supplier adopted a centralized reverse logistics hub to handle returns from dealerships across the country. This hub was equipped with diagnostic tools, repair stations, and recycling facilities. The consolidation of return processing reduced transportation costs by 18% and increased parts reuse by over 35%. Not only did this drive down costs, but it also contributed to the company’s sustainability goals by reducing landfill contributions.
3. Pharmaceutical Sector
A pharmaceutical wholesaler developed a compliant reverse logistics system to handle expired and recalled drugs. Given the strict regulatory environment, the system was designed with end-to-end traceability and secure disposal mechanisms. Through strategic partnerships with certified waste handlers and software solutions for tracking, the wholesaler ensured compliance with FDA and DEA regulations, minimized liability, and improved accountability across the supply chain.
The Financial Impact of Reverse Logistics in B2B Supply Chains
Reverse logistics, when executed efficiently, becomes a profit center rather than a cost center. Key financial benefits include:
- Recovery of value from returned goods: Reselling refurbished or repackaged goods.
- Reduced write-offs: Improved inventory control and earlier detection of defective stock reduce obsolescence.
- Lower operational costs: Optimized transportation and warehouse space usage reduce logistics overhead.
- Tax benefits and incentives: Certain sustainability practices in reverse logistics may qualify for government incentives or tax deductions.
In fact, studies by the Reverse Logistics Association show that companies that strategically implement reverse logistics can increase overall supply chain efficiency by up to 12%.
Future Trends in Reverse Logistics
As B2B supply chains continue to evolve, reverse logistics will become even more integral to business success. Here are some emerging trends shaping the future:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-driven systems can predict return rates, automate sorting, and improve route planning. Machine learning algorithms analyze customer behavior to identify products most likely to be returned and help businesses take preventive actions—such as improving product design or providing better pre-sale information.
2. Blockchain for Transparency
Blockchain can offer a secure and transparent method for tracking returns, especially in high-value or regulated industries. It ensures authenticity, prevents fraud, and maintains a tamper-proof record of each transaction in the reverse logistics process.
3. Circular Economy Integration
Businesses are increasingly aligning reverse logistics strategies with circular economy principles. This means not just recycling, but designing products for disassembly, reuse, and regeneration. Companies like HP and Dell are leading examples of this approach in action.
4. Green Logistics and Carbon Tracking
With ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) frameworks becoming more important to investors, businesses will increasingly focus on carbon footprint tracking in reverse logistics. Optimizing return routes and using eco-friendly packaging and transportation methods will become standard practices.
Best Practices for Mastering Reverse Logistics in B2B
- Start with a Clear Policy: A transparent and detailed return policy helps set expectations and streamline the process.
- Invest in Training: Employees across departments should be educated on the reverse logistics process and its strategic importance.
- Use Modular Packaging: Design packaging to facilitate easy returns and reduce damage during reverse transit.
- Incorporate Feedback Loops: Use data from returns to inform product design, marketing strategies, and customer service improvements.
- Focus on End-to-End Integration: Reverse logistics should not be treated as an afterthought. Integrate it with forward logistics, customer service, and product lifecycle management for maximum impact.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Reverse Logistics
In the ever-evolving world of B2B supply chains, reverse logistics is no longer just a necessity—it’s a strategic asset. From boosting customer loyalty and driving cost efficiencies to enhancing sustainability and regulatory compliance, the benefits of a well-executed reverse logistics strategy are vast.
By embracing technology, standardizing processes, and staying ahead of emerging trends, B2B companies can unlock the full potential of reverse logistics. It’s not just about handling returns—it’s about creating value at every step of the supply chain journey.
Reverse logistics isn’t just the end of the line—it’s the start of a smarter, more sustainable, and more resilient supply chain.





