Introduction to Edge Computing
Edge computing represents a transformative approach in the realm of technology, particularly within B2B infrastructure strategies. At its core, edge computing involves decentralizing data processing by placing computational resources closer to the location where data is generated, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This shift not only enhances responsiveness but also allows businesses to optimize bandwidth usage, reduce latency, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data from multiple sources is transmitted to a centralized server for processing, edge computing harnesses the power of localized data handling. By executing operations at or near the data source, organizations can achieve real-time analytics and decision-making capabilities that are essential in today’s fast-paced digital environment. This model is particularly pertinent for industries that rely heavily on IoT devices, autonomous systems, and real-time data analysis.
The relevance of edge computing in the current technological landscape cannot be overstated. With the exponential growth of connected devices generating vast amounts of data, there is an increasing demand for solutions that can process information quickly and efficiently. Businesses are recognizing that a decentralized computing model allows them to scale their operations while maintaining control over data privacy and security. Furthermore, edge computing is inherently designed to support advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, enriching the capabilities of B2B infrastructures.
In light of these developments, companies are encouraged to consider how edge computing can enhance their infrastructure strategy. By embracing this innovative approach, organizations not only position themselves to meet immediate operational challenges but also ensure their long-term competitiveness in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
The Importance of B2B Infrastructure in a Digital Era
In today’s highly interconnected business environment, the significance of a robust B2B infrastructure cannot be overstated. As organizations navigate the complexities of digital transformation, the evolution of B2B transactions has become increasingly reliant on advanced technological frameworks. Businesses are no longer confined to traditional processes; instead, they are embracing innovative solutions that enable seamless interactions and integrations with various stakeholders.
The shift towards digital platforms has fundamentally altered how B2B transactions occur. Companies are increasingly utilizing cloud-based solutions, advanced data analytics, and real-time communication tools to facilitate their operations. These modern infrastructure strategies not only streamline processes but also enhance efficiency and competitiveness in the marketplace. Building an effective B2B infrastructure allows organizations to harness technology, ensuring that they remain agile and responsive to changing market demands.
Furthermore, a well-designed B2B infrastructure fosters improved collaboration and communication between partners. By leveraging technology, businesses can create more effective workflows and share critical data effortlessly. Such enhancements lead to better decision-making and greater alignment on objectives. As organizations adopt these modern strategies, they can expect to see marked improvements in overall business outcomes, including faster transaction times, reduced operational costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, companies that invest in enhancing their B2B infrastructure will find themselves better equipped for future challenges. This strategic investment not only secures a competitive edge but also positions organizations to thrive in an era defined by speed and adaptability. In summary, the importance of B2B infrastructure in a digital era is crucial for sustainable growth and long-term success in today’s fast-paced business environment.
The Benefits of Edge Computing for B2B Companies
Edge computing has emerged as a crucial component of modern infrastructure strategies for B2B companies, addressing the growing demands for real-time data processing and improved operational efficiency. One of the most significant advantages of edge computing is its ability to reduce latency. By processing data closer to the source, businesses can minimize delays that occur when data must travel to a centralized cloud location. This reduced latency is especially beneficial for applications requiring immediate decision-making, such as in IoT devices and real-time analytics.
Another key benefit lies in enhanced data handling efficiency. By utilizing edge computing, companies are empowered to process large volumes of data locally, thereby decreasing the reliance on bandwidth-intensive cloud services. This localized processing not only streamlines operations but also enables firms to manage and analyze data in near real-time. For instance, manufacturing companies can deploy edge devices on the shop floor to monitor processes continuously, leading to more informed decision-making and increased production yields.
Furthermore, edge computing provides improved security for sensitive data. By keeping data processing at the edge of the network, B2B companies can reduce the surface area exposed to cyber threats that typically target centralized cloud systems. This distributed approach helps in safeguarding critical information and ensures compliance with data privacy regulations. A relevant case study is found in the healthcare sector, where edge computing allows for secure patient data management while simultaneously maintaining operational efficiency.
Lastly, effective bandwidth management is a pivotal advantage of edge computing. As the volume of data generated continues to rise, businesses can alleviate network congestion by processing data locally and selectively transmitting only essential information to the cloud. This optimization leads to reduced costs and higher throughput, enabling organizations to allocate resources more effectively.
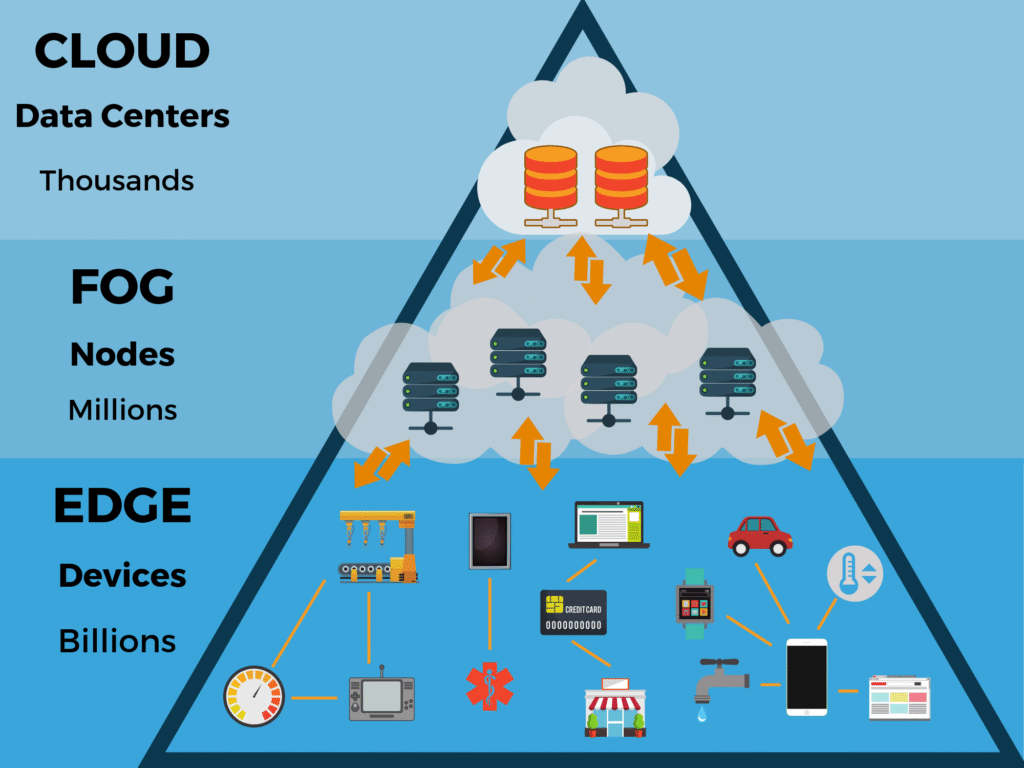
Challenges in Implementing Edge Computing
As businesses increasingly recognize the potential of edge computing to enhance their operational efficiency, several challenges arise when integrating these technologies into B2B infrastructure strategies. One of the foremost concerns is scalability. Edge computing requires a delicate balance between processing power and geographical placement of computing resources. As organizations grow and their data requirements expand, effectively scaling edge solutions can present significant logistical and technical challenges. Companies must carefully plan their edge architecture to ensure that it can accommodate future growth without compromising performance.
Interoperability is another critical issue facing B2B companies when implementing edge computing. Various devices, applications, and platforms may use different protocols and standards, making seamless integration challenging. Ensuring that edge solutions can communicate effectively with existing systems is vital for maximizing operational efficiency. Organizations should prioritize compatibility by selecting platforms that support standardized protocols, thereby minimizing integration challenges.
Data governance further complicates the deployment of edge computing solutions. As data is processed at the edge rather than centralized data centers, organizations face heightened risks in terms of data security and compliance. Data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), necessitate rigorous governance frameworks. Organizations must implement robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive information processed at edge locations.
To navigate these challenges, businesses should adopt best practices such as conducting thorough assessments of their current infrastructure, investing in scalable solutions, and establishing clear policies regarding data governance. By proactively addressing these potential pitfalls, companies can better position themselves to harness the full benefits of edge computing within their B2B infrastructure strategies.
Integration of Edge Computing with Existing Systems
Integrating edge computing into an organization’s existing IT infrastructure can drive significant improvements in performance, responsiveness, and overall operational efficiency. To ensure a seamless transition, businesses must take several essential steps that encompass evaluating current capabilities, planning for hybrid environments, and ensuring compatibility with legacy systems.
The first step in integration involves a thorough assessment of the current IT infrastructure. Businesses should conduct an inventory of existing hardware and software, identifying strengths and weaknesses in the system. Understanding capacity limitations and potential bottlenecks is vital, as these insights will inform the transition strategy to edge computing. A keen focus on existing data traffic patterns and latency issues will also help frame the integration process, highlighting specific areas where edge computing can provide immediate benefits.
Next, planning for a hybrid environment is crucial. Most organizations today operate with a mix of on-premises, cloud-based, and edge computing solutions. A successful integration strategy will effectively leverage the benefits of edge computing while maintaining the necessary functionality of existing systems. It is essential to develop a detailed roadmap that outlines the phases of integration, including pilot projects, expanded deployment, and full-scale implementation timelines.
Ensuring compatibility with legacy systems is another significant factor in the integration process. Older systems may pose challenges when interfacing with edge technologies, potentially hindering the overall effectiveness of the integration. Therefore, it may be necessary to upgrade or replace outdated systems or incorporate middleware solutions that can bridge the gap between legacy technologies and new edge computing resources.
Finally, collaboration across departments is paramount to facilitate effective integration. It is essential to involve key stakeholders from IT, operations, and business management throughout the process. This collaboration ensures that diverse perspectives are considered, and any potential impacts on current workflows are adequately addressed, ultimately leading to a smoother transition to edge computing.
Future Trends in Edge Computing and B2B Infrastructure
The landscape of edge computing is rapidly evolving, bringing forth a multitude of advancements that will significantly impact B2B infrastructure strategies in the forthcoming years. One of the most noteworthy trends is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning at the edge. By processing data closer to its source, businesses can leverage AI algorithms to analyze information in real-time, enabling immediate decision-making and enhancing operational efficiency. This capability not only reduces latency but also optimizes bandwidth usage, allowing enterprises to harness insights from critical data without overwhelming central systems.
Moreover, the burgeoning Internet of Things (IoT) is set to play a pivotal role in shaping edge computing dynamics. As more devices become interconnected, the volume of data generated will escalate exponentially. This trend necessitates robust edge computing solutions, which can efficiently manage, process, and analyze data on-site. By employing edge infrastructure, organizations can ensure timely responses to changing conditions and improve the reliability of their B2B operations. The ability to deploy IoT applications at the edge will facilitate innovations in tracking systems, supply chain management, and predictive maintenance, thereby enhancing overall business outcomes.
Another significant factor contributing to the advancement of edge computing is the anticipated rollout of 5G technology. The enhanced speed and reduced latency offered by 5G networks will catalyze the adoption of edge solutions among B2B companies. With the greater ability to transfer large volumes of data instantly, businesses can implement more sophisticated applications that require immediate access to information. Consequently, the incorporation of 5G in edge computing is likely to unlock new opportunities for real-time analytics, autonomous systems, and more intricate integrations within business ecosystems.
As these trends unfold, it is clear that edge computing will be an indispensable element of future B2B infrastructure strategies. Companies that embrace these advancements will position themselves favorably in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Real-World Case Studies of Edge Computing in B2B
Edge computing has started to redefine how businesses operate, particularly within the B2B sector. This section explores several compelling case studies that demonstrate the efficacy of edge computing in addressing specific challenges faced by enterprises today.
One notable example is a leading logistics company that faced persistent delays in their supply chain operations due to latency issues in data transmission. By implementing edge computing solutions, they deployed localized data processing and analytics closer to their IoT devices, which significantly improved real-time visibility. As a result, they successfully streamlined their operations and shortened delivery times, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
Another impactful case is that of a manufacturing firm struggling with equipment downtime due to unanticipated maintenance needs. The inefficiencies were traced back to a lack of real-time monitoring. By integrating edge computing with their existing machinery, they established a system for predictive maintenance. Edge devices processed data from sensors on the machines in real time, enabling the company to anticipate and resolve issues before they led to costly failures. Consequently, they reported a 25% reduction in downtime, translating to increased productivity and profitability.
Additionally, a financial services company faced challenges in handling vast volumes of transactions securely while ensuring compliance with regulations. The organization opted for an edge computing model to manage sensitive data at local nodes, minimizing the risk associated with data transmission to centralized data centers. This strategy not only improved data security but also enhanced transaction processing speed, positioning the company as a more competitive player in the finance industry.
These case studies illustrate how edge computing can offer tailored solutions to specific challenges, resulting in significant operational improvements and competitive advantages for B2B enterprises.
Best Practices for B2B Companies Adopting Edge Computing
As B2B companies increasingly recognize the importance of edge computing in their infrastructure strategies, implementing this technology effectively becomes crucial. To ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of edge computing, businesses can adopt several best practices throughout their deployment process.
First, it is vital to conduct a thorough assessment of specific business needs and the existing infrastructure. Understanding the unique requirements of different departments and how they can benefit from edge solutions allows for targeted implementations. Businesses should map out where data is generated and the desired outcomes of edge computing, which helps identify optimal deployment locations.
Security is another significant aspect when adopting edge computing. With a distributed network, vulnerabilities may increase, making it essential to implement robust data protection protocols. Businesses should regularly conduct security audits and invest in encryption technologies to ensure that sensitive information is safeguarded at all edge locations. Additionally, ongoing employee training regarding cybersecurity practices can mitigate human error risks.
Another key practice involves establishing a comprehensive monitoring system for performance evaluation. Implementing real-time monitoring tools enables organizations to proactively identify and address performance bottlenecks at the edge. This approach aids in maintaining optimal service levels while minimizing latency issues that might arise from a decentralized infrastructure.
Continuously optimizing edge solutions is critical for drawing maximum value from the investments made in edge computing. B2B companies should regularly assess their edge applications and infrastructure to identify opportunities for enhancements. This involves leveraging data analytics to gain insights into performance trends, user behavior, and workload distribution, ultimately guiding strategic adjustments.
By adhering to these best practices, B2B companies can facilitate successful integration of edge computing within their infrastructure strategies, ensuring they remain agile and competitive in the evolving technological landscape.
Conclusion: Embracing Edge Computing in B2B Strategies
As we consider the transformative potential of edge computing within B2B infrastructure strategies, it is evident that this technology is no longer a futuristic notion but a critical component for modern enterprises. The decentralized model offered by edge computing allows businesses to process data closer to its source, reducing latency and enhancing response times. This capability empowers organizations to harness real-time data analysis, which is pivotal in making informed decisions quickly in a fast-paced digital marketplace.
Moreover, integrating edge computing enhances operational efficiency by alleviating the burden on centralized cloud servers, thereby optimizing bandwidth and reducing costs. This is particularly beneficial for industries requiring immediate data processing, such as manufacturing and logistics. By adopting edge technology, businesses can streamline their operations, resulting in improved productivity and resource utilization.
Furthermore, edge computing plays a significant role in bolstering data security. By processing sensitive information nearer to its origin, businesses can mitigate risks associated with data transfer and centralization. This local processing capability is vital for maintaining compliance with data regulations and safeguarding customer privacy, which are growing concerns in today’s digital landscape.
The competitive advantages offered by edge computing are increasingly recognized by industry leaders. Those who invest in and implement these solutions are better positioned to adapt to market fluctuations, innovate faster, and deliver superior customer experiences. Therefore, it is essential for B2B leaders to embrace edge computing as an integral part of their infrastructure strategy.
In light of these insights, businesses should explore various edge computing solutions that align with their unique needs and objectives. By integrating this technology into their infrastructure, organizations can unlock new avenues for growth and ensure their readiness for the challenges of tomorrow. The time to act is now—an investment in edge computing is an investment in future success.